Under the Sea: Fish & their Nutritional Values

“Fish is good for your brain, and can help you get good results. Come, eat more, eat more!” Malaysians should be familiar with this statement during mealtimes or family gatherings. Fish is delicious and easy to prepare in various methods, as it can be either grilled, fried, steamed, baked etc and pairs well with different vegatables and grains.
Types of Fish & Nutritional Values
However, the risks associated with regular consumption of fish is that it contains mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Thus, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and FDA has advised women of childbearing age, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and children to avoid fish with higher mercury contamination such as swordfish, shark, king mackerel, tilefish. The 12 best fish list with great nutrition and safety profiles are as listed below:
- Alaskan salmon
- Cod Fish
- Herring
- Mahi-mahi
- Mackerel (lower mercury Atlantic or smaller mackerel)
- Perch
- Rainbow trout
- Sardines
- Stripped bass
- Tuna
- Wild Alaskan pollock
- Arctic char
High quality protein

Yes, fish is indeed a nutritious food. Fish contains low fat high quality protein that can be equivalent to meat and poultry. Protein is important as it can help maintain healthy muscles, organs and blood vessels. Example of fish especially high in amino acid lysine are cod fish and sardines, and amino acid lysine may be deficient in rice diets with little animal protein. So, what are the benefits of lysine?
Benefits of Lysine include:
- Lysine may reduce cold sores duration and frequency, but evidence is inconsistent
- Lysine may help reduce anxiety and stress level
- Lysing may improve schizophrenia symptoms
- Lysine may assist in calcium absorption and reduce loss of calcium in urine
- Lysine is essential for collagen formation and helps in wound healing and reducing recovery time
- Other benefits of lysine include anti-cancer effects, improvement in blood glucose level and blood pressure reduction
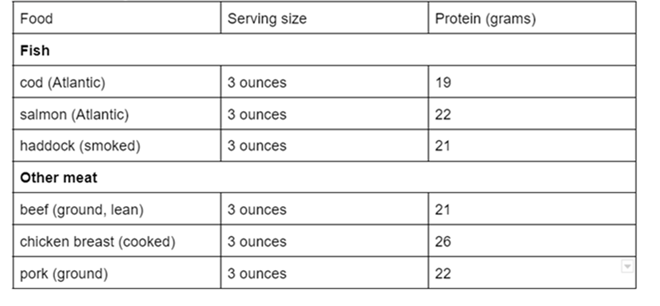
Table: Protein in grams between fish and other meat
Omega-3 fatty acids

Fish is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids vital for brain development and cognition and heart health. Studies have shown that oily or fatty fish may lower the risk of coronary heart disease mortality among adults, thus reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Omega-3 fatty acids are not produced in our bodies, thus it is required to be obtained from diet. Some fish such as salmon, trout, herring contain high polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) also known as omega 3 fatty acid, which can help provide specific health benefits, notably improving cardiovascular disease. There are 2 types of omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, which are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). For general health, a target of 200 to 500mg daily of DHA and EPA can be taken from food and/or supplements.
Benefits of DHA and EPA in omega-3 fatty acids are:
- Improve blood flow and lower blood pressure
- Improve heart health, thus reducing heart attack and risk of stroke
- Decrease triglycerides level, increasing HDL (good) cholesterol
- Improve behaviour and attention span for adults with ADHD
- Essential for brain development and cognition (eye development) for infants. Taking 600 to 800 mg of DHA daily during pregnancy reduces risk of early preterm birth.
- Anti-inflammatory effects, counteracting symptoms such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Improve eye conditions such as dry eyes and diabetic retinopathy.
- Lower risk of certain cancers including breast, colorectal and prostate cancer.
- Prevent or slow Alzheimer’s disease and dementia- more gray matter in brain centers controlling memory and emotion are found in people who consume fish regularly
- Maintain healthy sperm and motility
- omega-3 may help combat depression
Vitamins & Minerals

Fish also contains vitamins such as vitamin D and B2 (riboflavin), and minerals (i.e. iron, iodine, magnesium, and potassium). The American Heart Association also recommends consumption of fish at least 2 times per week in our diet.
Vitamins in fish:
- Vitamin A: Necessary for healthy vision and treatment of eye disease. Vitamin A is also essential for normal growth, healthy skin, bones, teeth and reproduction
- Vitamin B complex:
- Vitamin B complex is associated with healthy nervous system
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) helps convert food into energy, healthy skin, hair, blood and brain
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) helps make red blood cells and improves sleep, appetite and mood
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) breaks down fatty acids and amino acids, and helps make red blood cell
- Vitamin D: fat soluble vitamin that strengthens and form bones and teeth
- Vitamin K: Prevents internal bleeding and stimulates blood coagulation
Minerals in fish:
- Calcium: For strong bones and blood clotting
- Magnesium: Maintain normal nerves and muscle function and healthy immune system
- Selenium: potent antioxidant protecting cell damage, reduce inflammation and enhance immunity. Selenium can also counteract the toxicity of heavy metals such as mercury
- Zinc and Iron: Both zinc and iron are required for cell growth and immune system Iron is essential for red blood production
- Potassium: Regulates biological pressures and muscle contraction
- Iodine: maintains thyroid gland function
A WORD FROM DOC2US
If you have any questions related to nutrition, vitamins, or supplements you can consult our professional doctors and healthcare professionals on DOC2US. DOC2US is a mobile application that allows you to talk to a doctor or any healthcare professionals via text chat at any time and from anywhere. For better communication, you can even send our online doctor images or voice messages related to your medical inquiry.
Download DOC2US app on Apple App Store, Google Play Store and Huawei App Gallery; or use our web chat at https://web.doc2us.com/
Note: DOC2US is not for medical emergencies. In the event of urgent medical conditions, please call 999.
Disclaimer: As a service to our users and general public, DOC2US provides health education contents. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Reference:
- Healthline. 12 Best Types of Fish to Eat. Available from https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/11-best-fish-to-eat#mackerel
- Healthline. 4 Impressive Health Benefits of Lysine. Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/lysine-benefits#TOC_TITLE_HDR_8
- Allina Health. Meat, poultry and fish. Available from https://www.allinahealth.org/health-conditions-and-treatments/eat-healthy/nutrition-basics/protein/meat-poultry-and-fish
- Healthline. 12 Health Benefits of DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid). Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/dha-benefits#TOC_TITLE_HDR_12
- Healthline. 11 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Eating Fish. Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-health-benefits-of-fish#TOC_TITLE_HDR_6
- Washington State Department of Health. Health Benefits of Fish. Available from https://www.doh.wa.gov/communityandenvironment/food/fish/healthbenefits#:~:text=Fish%20is%20filled%20with%20omega,part%20of%20a%20healthy%20diet.








