Our lower back
Our lower back functions to support most of the weight of our upper body. It includes five vertebrae in the lumbar region, with intervertebral discs (round, rubbery pads) in the spaces between each vertebra, that act like shock absorbers throughout the spinal column to cushion the bones during body movements. Ligaments are bands of tissue that hold the vertebrae in place while tendons attach the muscles to the spinal column. Thirty-one pairs of nerves are rooted to the spinal cord and they control body movements and transmit signals from the body to the brain.4
Lower back pain
Back pain, which most commonly occurs in our lower back, can cause disruption to our day-to-day activities and quality of life. It ranges from a dull, constant ache to a sharp or shooting pain.
Symptoms:
- Muscle ache or shooting/stabbing pain1
- Limited flexibility and range of motion/inability to stand straight
- Pain or weakness in lower limbs
There are two types of back pain:4
- Acute (short-term back pain)
- Usually lasts a few days to a few weeks
- Resolves on its own within a few days with self-management and usually does not cause any long-term complications
- Chronic (long-term back pain)
- Pain that continues for 12 weeks or longer, with or without intervention
- Does not always equate to medically serious underlying cause
What might have caused this? 3
Lower back pain can be caused by injuries/sprains. It can also be caused by certain medical conditions or as a symptom that indicates some more serious underlying diseases.
Who is at risk?4
|
Elderly As we age, our bone density, muscle elasticity and tone decrease. The ability to cushion the vertebrae also decreases as the intervertebral disc begin to lose fluid and flexibility. |
Obese/overweight The constant extra stress as our lower back need to support the upper body weight contributes to lower back pain. |
|
Pregnant woman Posture changes, hormone changes, increased emotional stress and weight gain contribute to lower back pain in pregnancy.2 |
Doing physically demanding work The ones who are always exposed to heaving lifting, pushing or pulling are more prone to lower back injury/pain. |
|
Sedentary lifestyle Often the office workers will sit on a chair for hours and this can lead to straining of lower back. Poor sitting posture or chair with minimum back support also worsens the condition. |
Inactive/poor physical fitness Weak back and abdominal muscles may not properly support the spine and this results in most of the upper body weight relying solely on the lower back. |
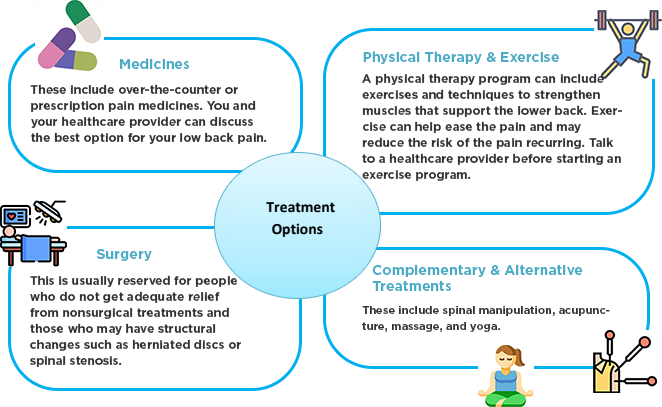
What are treatments available?4
When to see a doctor:3
- The back pain lasts longer than 4 weeks
- Acute back pain and inflammation does not improve or worsens within 72 hours of selfcare1
- When you had a fall/blow that may potentially have caused a head injury Burning with urination or blood in your urine
- History of cancer
- Redness or swelling on the back or spine
- Unexplained fever with back pain
- You use steroids or intravenous drugs
To learn more, please visit these websites:

https://www.myhealthmylife.com.my/ https://www.menshealth.com.my/
References:
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Back Pain Information Page. Available at: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/All-Disorders/Back-Pain-Information-Page. Accessed on October 07, 2020.
- WebMD. Back Pain in Pregnancy. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/baby/guide/back-painin-pregnancy#1 Accessed on October 07, 2020.
- MedlinePlus. Low back pain - acute. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007425.htm Accessed on October 07, 2020.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Low Back Pain Fact Sheet. Available at: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Low-Back-Pain-Fact-Sheet#3102_4 Accessed on October 07, 2020









