What is infertility?
Infertility is a condition where a couple is unable to conceive even after a year of regular unprotected sex. It is surprisingly common among couples - affecting up to 1 in every 7 couples. Infertility can be divided into two categories, Primary and Secondary Infertility. Primary Infertility refers to the condition where a person has never conceived a child before whereas Secondary Infertility refers to the condition where a person has conceived in the past but is currently facing difficulties conceiving again.

What causes infertility?
Unlike common belief, infertility can be caused by the male reproductive system, the female reproductive system or both.
Male infertility may be due to:
- Obstructions in the reproductive system affecting the ejection of semen. These blockages may occur in the seminal vesicles or ejaculatory ducts which carry the semen.
- Disorder in the reproductive hormones produced by the hypothalamus and pituitary glands, which affects normal testicular functions.
- Reduced number of sperms or inability to produce sperms. This can be caused by varicoceles*, trauma to the testes or other medical treatments that may have damaged the cells responsible for sperm production, such as chemotherapy.
- Conditions that cause changes in the sperms’ shape (morphology) and movement (motility).
* Varicoceles is a condition where the veins on the testicles are too thick. This condition causes the overheating of the testicles, which may affect the number and morphology of the sperm.
Female infertility may be due to:
- Obstructions in the fallopian tubes, which may be blocked, swollen or open. Fallopian tubes are the pathways for the ova to move from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Disorder in the reproductive hormones produced by the hypothalamus and pituitary glands, which affects normal ovarian functions.
- Uterine disorders such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids (small growths) and uterine cysts.
- Thyroid problems (overactive or underactive) that may prevent ovulation.
- Abnormalities in the ovaries such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)* or other reproductive disorders.
* Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition where the ovaries do not ovulate regularly. Women with PCOS often have excess androgen (male hormone) in their bodies. It is also the most common cause of infertility in women.
Other causes of infertility include:
- Age (over 35 for women and 40 for men)
- Diabetes
- Stress
- Substance abuse (alcohol, drugs)
- Weight problems
- A side effect of medicines
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) and many others

Image Credit: Link
Addressing Infertility
Addressing infertility is important because fertility decreases with age. Fertility treatments start with understanding the cause of infertility. This involves a range of different tests for both partners such as physical examinations and fertility tests.
Fertility tests for men:
- Semen analysis to check for low sperm count, sperm morphology and motility.
- Chlamydia tests. Chlamydia is a STI that affects fertility.
Fertility tests for women:
- Blood tests to check the hormones that regulate menstruation.
- Chlamydia tests. Chlamydia is a STI that affects fertility.
- An ultrasound test to check the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tube. This is to check for possible blockages in the fallopian tube or other conditions such as endometriosis and fibroids.
Fertility Treatments
3 main fertility treatments can be given, based on the individual’s condition:
- Medicine
- Surgery
- Assisted Conception
Fertility Medicine:
These medicines treat infertility by increasing or reducing specific hormones in our bodies.
Surgery for male infertility:
- Epididymal blockage surgery. The epididymis is a coil-like structure in the testicles that help store and transport sperm.
- Surgical extraction of sperm.
Surgery for female infertility:
- Fallopian tube surgery if there are any blockages in the fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopic surgery to treat endometriosis or to remove any submucosal fibroids.
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling to treat PCOS
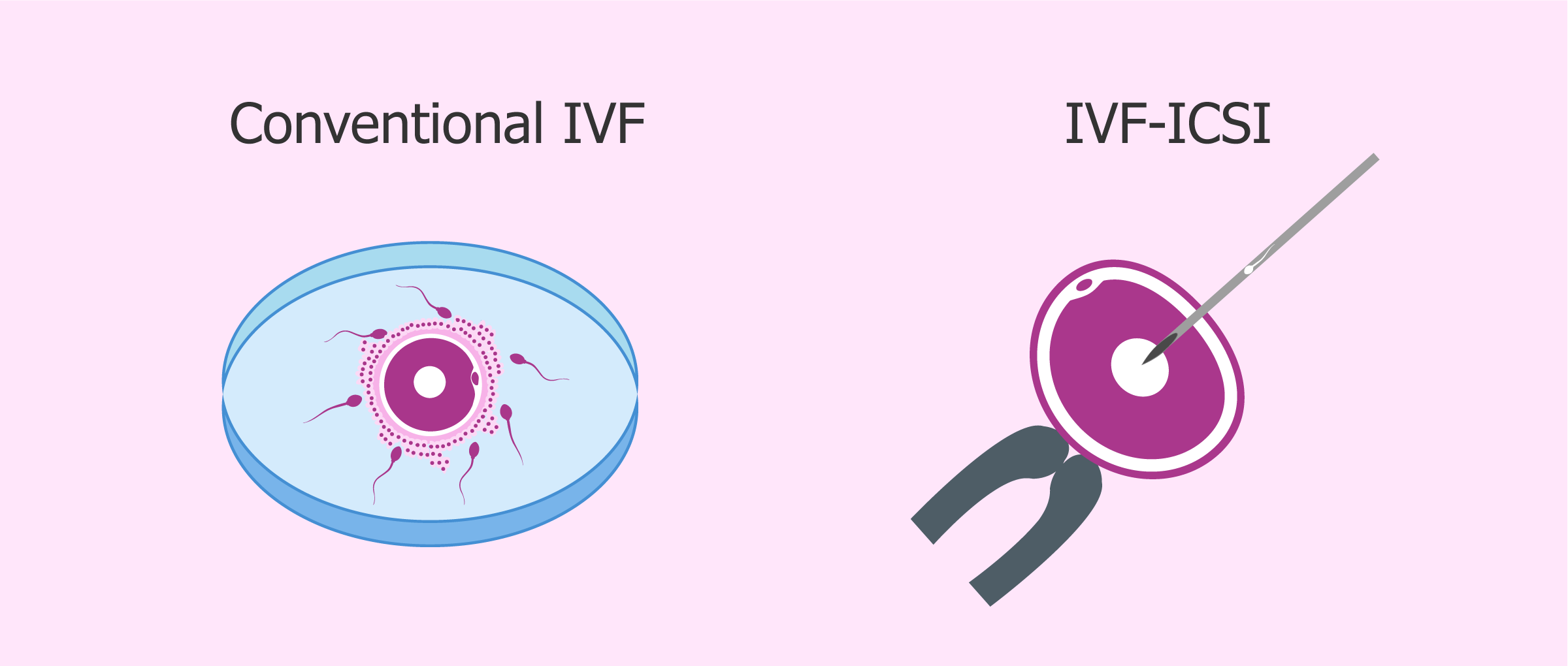
Image Credit: Link
Assisted Conception:
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
IUI involves the process of inserting sperm into the womb through a thin catheter after medicine or injection treatments.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
In IVF, fertility medicine is given to women to encourage ovulation. The eggs are then extracted and fertilised with sperm outside of the women’s body. The fertilised egg is then returned to the womb to grow.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
ICSI is one form of IVF and is designed for males with low sperm count. The sperm is inserted into the centre of the egg via a microneedle to fertilise it.
A word from DOC2US
If you have any questions related to OAB, you can consult our professional doctors and healthcare professionals on DOC2US. DOC2US is a mobile application that allows you to talk to a doctor or any healthcare professionals via text chat at any time and from anywhere. For better communication, you can even send our online doctor images or voice messages related to your medical inquiry.
Download DOC2US app on Apple App Store, Google Play Store and Huawei App Gallery; or use our web chat at https://web.doc2us.com/
Note: DOC2US is not for medical emergencies. In the event of urgent medical conditions, please call 999.
Disclaimer: As a service to our users and general public, Doc2Us provides health education contents. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
References
Cover image credit: Photo by Dreamstime








