 Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that are passed on to another person via unprotected sexual intercourse. The more commonly seen STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, genital warts, and genital herpes. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human papillomavirus (HPV), while not as common, are also STIs to be wary of. The two factors that increase risks of getting an STI are having multiple sex partners and having unprotected sex. People are often more apprehensive of the lady getting pregnant, rather than focussing on protecting themselves and their partners from STIs. This is thus a reminder that preventing STI transmission is just as important as, if not more important than, family planning (i.e. avoiding unwanted pregnancies).
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that are passed on to another person via unprotected sexual intercourse. The more commonly seen STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, genital warts, and genital herpes. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human papillomavirus (HPV), while not as common, are also STIs to be wary of. The two factors that increase risks of getting an STI are having multiple sex partners and having unprotected sex. People are often more apprehensive of the lady getting pregnant, rather than focussing on protecting themselves and their partners from STIs. This is thus a reminder that preventing STI transmission is just as important as, if not more important than, family planning (i.e. avoiding unwanted pregnancies). 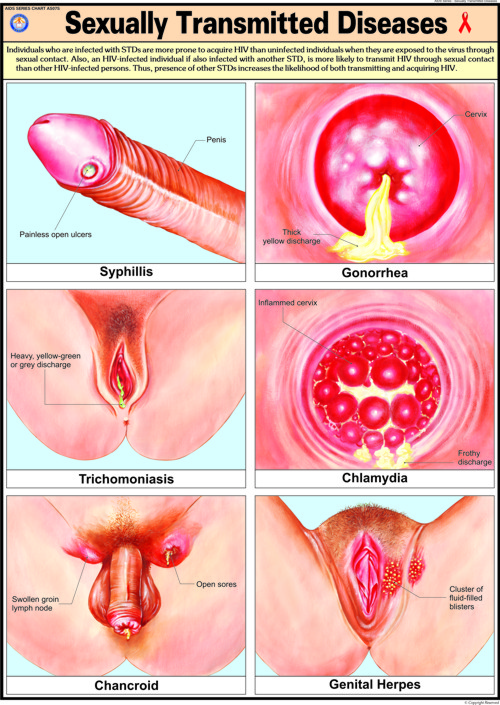 Signs that you might have an STI include a burning sensation while urinating, discharge from the penis (or vagina for ladies), and ulcers or warts on your genital area. It is however important to note that not everyone with an STI will be symptomatic. Therefore, if you are concerned that you or your partner may have an STI, please go for a screening test prior to initiating sexual intercourse. Avoiding STI transmission can be very easily achieved. Only have sexual intercourse with one committed partner, after ensuring that he/she is free from STIs. Using condoms can help to further reduce the risk of STI transmission if a partner's status cannot be ascertained, on top of helping to prevent pregnancies.
Signs that you might have an STI include a burning sensation while urinating, discharge from the penis (or vagina for ladies), and ulcers or warts on your genital area. It is however important to note that not everyone with an STI will be symptomatic. Therefore, if you are concerned that you or your partner may have an STI, please go for a screening test prior to initiating sexual intercourse. Avoiding STI transmission can be very easily achieved. Only have sexual intercourse with one committed partner, after ensuring that he/she is free from STIs. Using condoms can help to further reduce the risk of STI transmission if a partner's status cannot be ascertained, on top of helping to prevent pregnancies.  An important thing to note is that patients with STIs who are undergoing treatment should not engage in any sexual intercourse until after completion of treatment. Play safe!
An important thing to note is that patients with STIs who are undergoing treatment should not engage in any sexual intercourse until after completion of treatment. Play safe! This post was sponsored by Scott's Shavers.








