Most people infected with coronavirus have mild or moderate symptoms such as fever, cough, and shortness of breath. However, some of them may get severe pneumonia in the lungs.
What is pneumonia?

Pneumonia is a potentially life-threatening lung infection caused by organisms including bacteria, viruses or fungi. It causes the lungs’ air sacs (alveoli) to inflame and fill with fluid or pus. Often, it is spread via coughing, sneezing, touching or even breathing.
Pneumonia symptoms
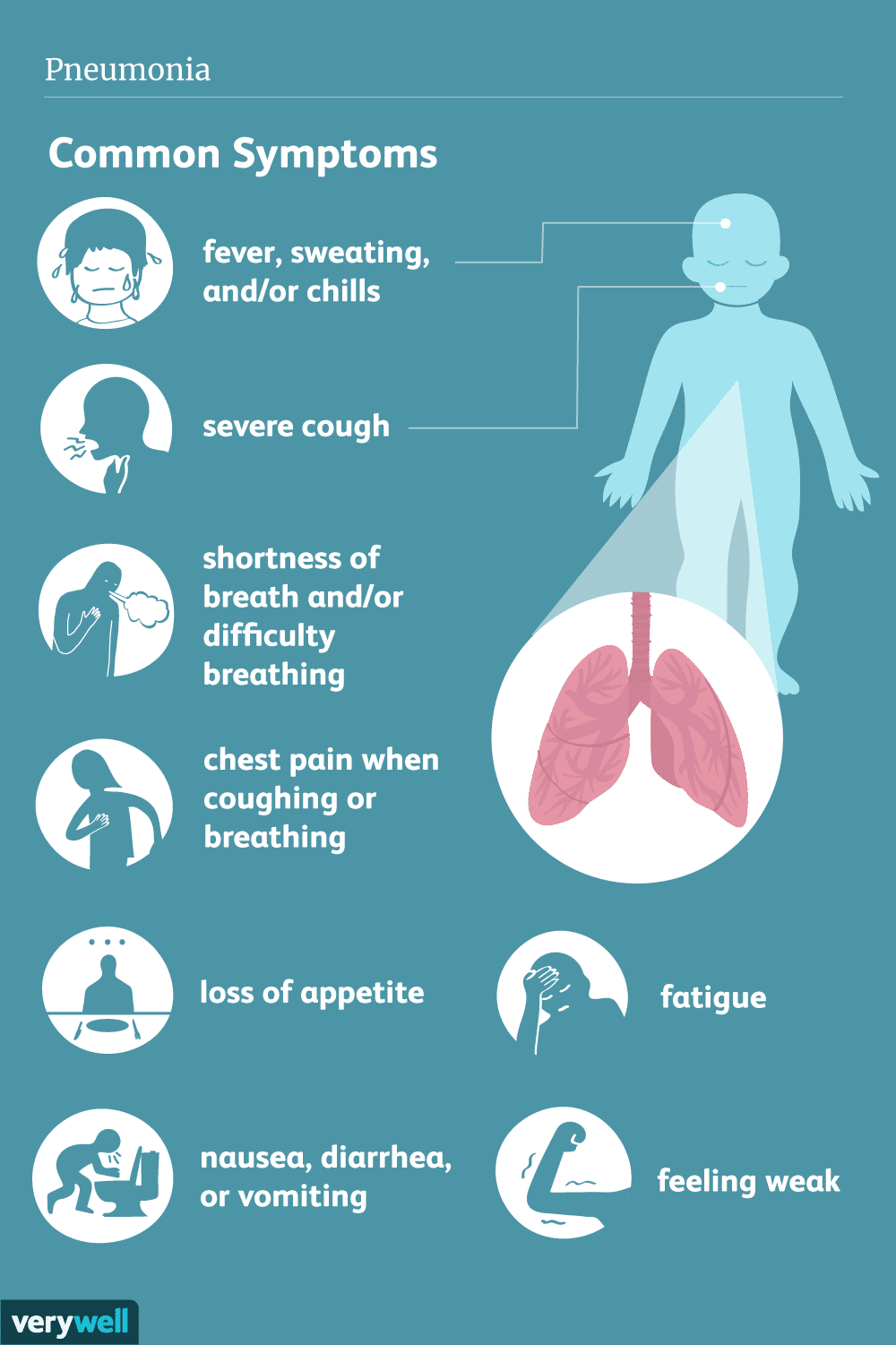
The symptoms of pneumonia can range from mild to severe; depending on factors such as the type of organism causing the infection, age group and overall health.
- Shortness of breath
- Productive cough
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Fever, sweating and chills
- Lower than normal body temperature (in adults age 65 and above and those with weaken immune systems
- Confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and above)
- Nausea, vomiting, restlessness, excessively sleepy, difficulty breathing and eating (in newborns and infants)
COVID-19 pneumonia symptoms
Fever, dry cough and tiredness are the common early signs of COVID-19. If the infection starts to cause pneumonia, you may also experience:
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat)
- Rapid breathing
- Dizziness
- Profuse sweating

How do I differentiate pneumonia from COVID-19?
As symptoms pf COVID-19 and pneumonia are similar, it can be difficult to tell which is the condition.
One study in China used CT scan and laboratory investigations to compare the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 pneumonia to other types of pneumonia. From the research, it was found that those with COVID-19 pneumonia were more likely to have:
- pneumonia affecting both lungs as opposed to just one
- "ground glass opacity" appearance of the lungs in CT scan
- abnormalities in liver function test
Am I at risk?
Anyone can get pneumonia, but many factors can increase your chances of getting it.
- Extreme ages; infants and children age two and below as well as elderly age 65 and above
- Chronic lung diseases such as asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis
- Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy
- People with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, organ transplant or long-term steroid use
- Difficulty swallowing, due to stroke, dementia or Parkinson’s disease which may result in aspiration of food, vomit or saliva into the lungs (aspiration pneumonia)
- Hospitalization; in intensive care, especially when on ventilator to breathe
- Exposure to certain chemicals, pollutants or toxic fumes
- Cigarette smokers
Causes
Pneumonia can be classified according to the types of germs and where one get the infection:
1. Community acquired pneumonia
This is the most common type of pneumonia. It may be caused by:
- Bacteria. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a type of pneumonia that can occur on its own or after a cold/flu. It may affect one part (lobe) of the lung causing lobar pneumonia
- Bacteria-like organisms. Mycoplasma pneumoniae can also cause pneumonia with milder symptoms. It is also known as walking pneumonia, which isn't severe enough to require bed rest.
- Viruses. Some viruses causing colds and flu can also cause pneumonia. They are the most common type of pneumonia in children under the age of 5.
- Fungi. Fungal pneumonia is common among people with chronic illnesses, weakened immune systems and those who inhaled large doses of the organisms.
2. Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP)
Prolonged stay in the hospital, such as those on ventilators can get hospital-acquired pneumonia. HAP can be difficult to treat as the bacteria causing it may be more resistant to antibiotics.
3. Healthcare acquired pneumonia
This bacterial type of pneumonia is an infection occuring in people who live in long-term care facilities or those who receive care in outpatients clinics (e.g. dialysis centres). Like HAP, healthcare acquired pneumonia can be caused by bacteria that are more resistant to antibiotics
4. Aspiration pneumonia
This usually occur when one inhale food, drink, saliva or vomit into the lungs. Conditions associated with altered or reduced consciousness, disturbed gag reflex, or ability to maintain the airway increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Examples include alcoholism, seizure, stroke, dementia, Parkinson's disease, general anaesthesia or head trauma.
Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection and preventing complications. Specific treatment depends on the type and severity of pneumonia, age and overall health.
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial pneumonia.
- Fever relievers such as paracetamol may be prescribed.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen the secretions and bring up phlegm.
- Get lots of rest so your pneumonia can resolve.
- In severe pneumonia, you may be given intravenous fluids and oxygen therapy to help you breathe better. A ventilator may be required if oxygen support is inadequate.
Prevention
1. Get vaccinated. Influenza vaccine can be taken annually. Pneumococcal vaccines are recommended for those in higher risk groups (children, elderly, immunocompromised individuals)

2. Practice good hygiene. Wash your hands regularly, especially after you go to the bathroom, as well as before and after you eat. Use a hand sanitizer that is at least 60% alcohol if you're unable to wash your hands/
3. Avoid anyone who is sick. If you are unwell, stay at home and avoid others as much as possible.
4. Stay away from smoke. This includes smoking and secondhand smoke.
References:
- Pneumonia| American Lung Association
- Pneumonia| Mayo Clinic
- Zhao D, Yao F, Wang L, Zheng L, Gao Y, Ye J, et al. A Comparative Study on the Clinical Features of Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia With Other Pneumonias. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):756-761. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa247
Image credit:
- https://cdn-img.health.com/sites/default/files/styles/medium_16_9/public/1484162465/GettyImages-471618065_0.jpg?itok=z_cmimWn&1519153887
- https://universityhealthnews.com/wp-content/uploads/pneumonia.jpg
- https://bit.ly/2UHVjQv
- https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/images/symptoms-testing/COVID19-symptoms-thumb.png
- https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2015/11/06/11/55/smoking-1026559_960_720.jpg
- https://healthunits.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/pneumonia-vaccine.jpg









